Rigid Pavement Design Aashto Method Flexible Rigid Pavement Design Excel Program YouTube Rigid Pavement Design By AASHTO Method pavement Design YouTube Get Answer Using The AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Method And The 3 Use The 1993 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Method Chegg 13 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Method Remaining Part YouTube Condition of pavements are rated with a present serviceability index PSI ranging from 5 perfect condition to 0 impossible to travel a Initial serviceability index Po Po is considered to be that PSI immediately after the pavement is open AASHTO values are 4 5 for rigid pavement and 4 2 for flexible pavement b
Design a new rigid pavement for a major interstate highway using the following conditions four lanes each direction Design ESALs The standard multiplier to calculate compound growth is 20 year design life 30 year design life 40 year design life Calculate the Effective Modulus of Subgrade Reaction k The SHA may use the design procedures outlined in the AASHTO Guide for Design of Pavement Structures or it may use other pavement design procedures that based on past performance or research are expected to produce satisfactory pavement designs AASHTO has approved a modification to the 1986 and 1993 rigid pavement design equations
13 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Method Remaining Part YouTube Flexible Pavement Thickness Design AASHTO Method Source Chapter 12 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Method YouTube Pavement Interactive SOLUTION Design Method For Rigid Pavement Studypool Flexible Pavement Design Aashto Method Example Lopsino Flexible Pavement Design Aashto Haqturbo Aashto Flexible Pavement Design Calculator Cherish Cline Flexible Pavement Design Aashto Method Streamingdas
Rigid Pavement Design Aashto Method
 Rigid Pavement Design Aashto Method
Rigid Pavement Design Aashto Method
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-HSnKKsWcR4/maxresdefault.jpg
The goal of structural design is to determine the number material composition and thickness of the different layers within a pavement structure required to accommodate a given loading regime This includes the surface course as well as any underlying base or subbase layers This section is focused on the structural design of new pavement
Templates are pre-designed files or files that can be used for numerous purposes. They can conserve time and effort by offering a ready-made format and layout for producing different type of content. Templates can be utilized for individual or expert tasks, such as resumes, invitations, leaflets, newsletters, reports, discussions, and more.
Rigid Pavement Design Aashto Method

Flexible Pavement Design Aashto Method Example Paasexpo

Flexible Pavement Thickness Design AASHTO Method Source Chapter

12 AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Method YouTube

Pavement Interactive

Flexible Pavement Design Aashto Method Example Lopsino

Flexible Pavement Design Aashto Haqturbo

To design a pavement by the AASHTO method a number of design parameters must be determined or assumed This section will explain the parameters required to design the pavement thickness of both concrete and hot mix asphalt roadways The same parameters can be used for input data in computer programs on pavement determinations

Chapter 8 Rigid Pavement Design Section 1 Overview 1 1 Rigid Pavement Types Different pavement types use different types of joints and reinforcement to control the forces acting on the concrete pavement These forces include drying shrinkage of the concrete environment changes and traffic loads
Many highway agencies use AASHTO methods for the design of pavement structures Current AASHTO methods are based on empirical relationships between traffic loading materials and pavement performance developed from the AASHO Road Test 1958 1961
Pavement Design Overview Rebecca S McDaniel November 9 2010 Plan Review types of pavements Features Advantages and Disadvantages Typical Distresses Common design techniques considerations AASHTO Mechanistic Empirical Resources Basic Pavement Types Flexible Rigid Composite Basic Pavement Types Flexible Rigid

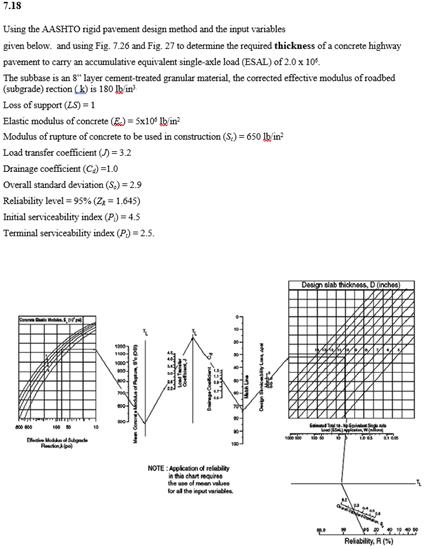
Load transfer device Dowels yes Aggregate interlock no Lane width 12 feet lower range Lane width 12 feet upper range Similar to flexible design Establish inputs and use Figure 3 7 to determine required slab thickness Iterative solution assume D to generate inputs
365 ADTT f L D T g Problem Statement Local practice is to use a granular subbase that will drain within a few hours The subbase has a resilient modulus of 15 000 psi when wet and 25 000 psi when dry The roadbed soil has a resilient modulus of 3000 psi during the 7 months wet months and 7000 psi the rest of the year The CivilWeb AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Spreadsheet completes the design of concrete roads or pavements in accordance with AASHTO 1998 It allows compliant concrete pavement designs to be completed in minutes with our unique design analysis tools showing the designer at a glance the optimum concrete pavement thickness
Road and Highways are a very significant cost for agencies to construct maintain and rehabilitate US Infrastructure worth 1 000 000 000 000 Pavement design is a very complex process that involves many variables as well as the variation of each variable It is one of the most complex Civil Engineering structures to design because we demand a